How Chronic Stress Affects Your Health and Autoimmune Conditions: What You Need to Know
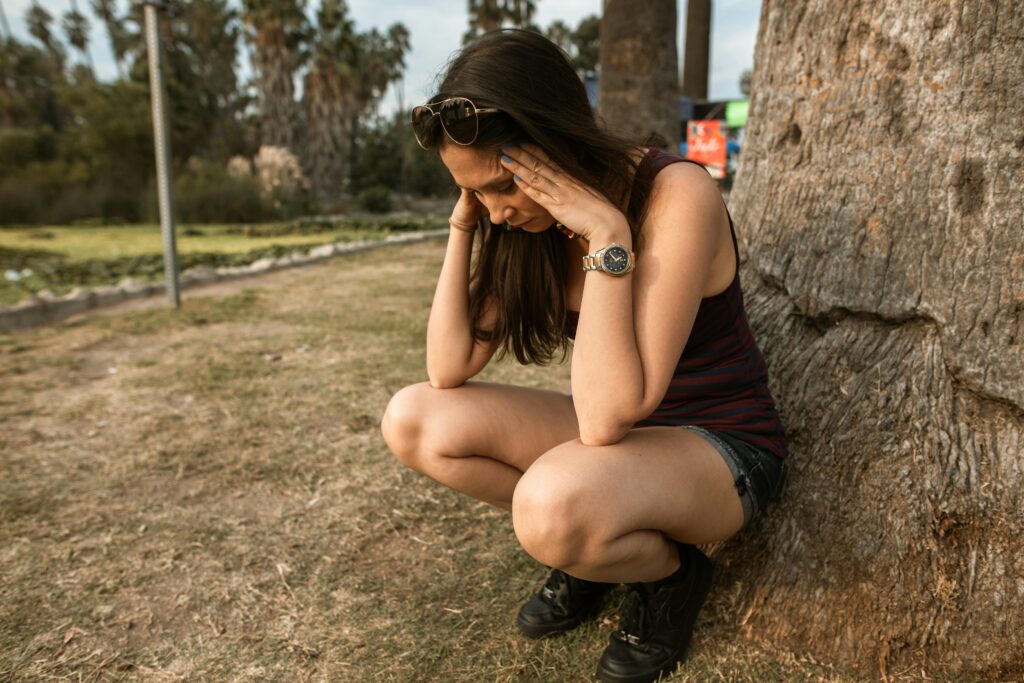

Stress is a normal part of life, but when it becomes chronic, it can wreak havoc on both your mental and physical health. For those managing autoimmune diseases, chronic stress isn’t just a nuisance—it can be a major trigger for flare-ups and exacerbate symptoms. In this post, we’ll explore the impact of stress on the body and share practical ways to manage it for a healthier, more balanced life.
1. What Is Chronic Stress?
In our fast-paced world, stress is more than an occasional feeling—it can be a constant companion. Chronic stress happens when the demands of life overwhelm our ability to cope, and it becomes a persistent presence in our day-to-day lives. Whether it’s work, relationships, or even health issues, long-term stress can seriously disrupt your body’s natural balance.
2. The Connection Between Stress and Autoimmune Diseases
Studies have shown that stress can directly impact the immune system. When we experience stress, our bodies release hormones like cortisol, which, when elevated for long periods, can weaken our immune response. This is especially concerning for those with autoimmune diseases, where the immune system is already malfunctioning. Chronic stress can trigger inflammation, aggravate symptoms, and even contribute to the onset of autoimmune conditions.
3. How Stress Manifests in the Body
Chronic stress doesn’t just stay in your mind—it impacts your entire body. Elevated cortisol levels can cause issues such as:
- Digestive problems (indigestion, bloating, or diarrhea)
- Increased appetite and weight gain
- Hormonal imbalances
- Fatigue and sleep disturbances
If left unchecked, chronic stress can lead to more severe health problems, including cardiovascular diseases and digestive disorders, further exacerbating autoimmune symptoms.
4. Coping with Chronic Stress: Break the Cycle
It’s easy to fall into harmful coping mechanisms when you’re stressed, like overeating or turning to alcohol. While these may offer temporary relief, they can create more stress in the long run and impact your overall health. Instead, try healthier habits:
- Exercise: Physical activity releases endorphins, which can help relieve stress and improve mood.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices like deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help bring your mind and body back into balance.
- Healthy Eating: Consuming nutrient-rich foods can support both your physical health and your mental resilience to stress.
- Sleep: Prioritizing quality sleep helps your body recover from daily stress and enhances overall health.
5. The Power of a Stress-Reduction Routine
Managing stress isn’t about eliminating it entirely but learning how to handle it before it affects your health. Simple daily practices like a morning walk in nature, controlled breathing exercises, or taking 10 minutes for mindfulness can make a significant difference over time. The key is consistency—small, regular actions can help keep chronic stress at bay and support your overall wellness.
Conclusion
Chronic stress can be overwhelming, but by understanding how it impacts your health, especially in the context of autoimmune diseases, you can take proactive steps to manage it. Remember, managing stress is a journey, not a sprint—much like managing autoimmune conditions. With the right strategies, you can live a more balanced and healthier life, free from the weight of chronic stress.